Publications
Highlights
(For a full list see below. Research Theses produced by the group)
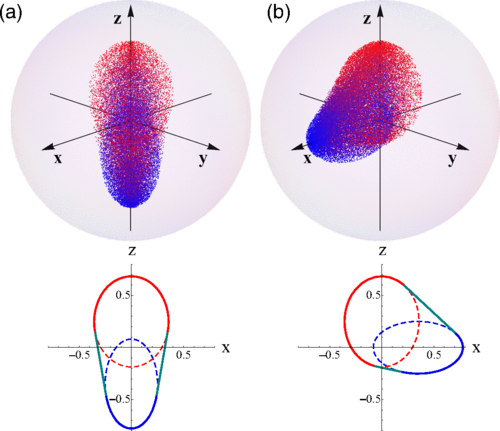
We examine, in correlated mixed states of qudit-qubit systems, the set of all conditional qubit states that can be reached after local measurements at the qudit based on rank-1 projectors. While for a similar measurement at the qubit the conditional postmeasurement qudit states lie on the surface of an ellipsoid, for a measurement at the qudit we show that the set of postmeasurement qubit states can form more complex solid regions. In particular, we show the emergence, for some classes of mixed states, of sets which are the convex hull of solid ellipsoids and which may lead to conelike and trianglelike shapes in limit cases. We also analyze the associated measurement-dependent conditional entropy, providing a full analytic determination of its minimum and of the minimizing local measurement at the qudit for the previous states. Separable rank-2 mixtures are also discussed.
M. Bilkis, N. Canosa, R.Rossignoli, N. Gigena
Physical Review A 99, 062119 (2019).
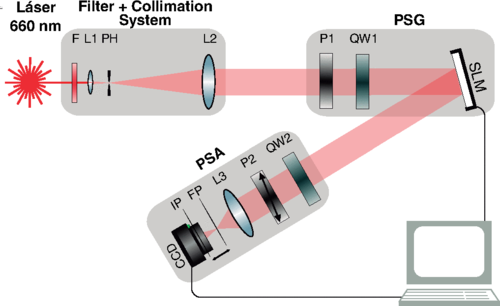
We present an experimental optical implementation of a parallel-in-time discrete model of quantum evolution, based on the entanglement between the quantum system and a finite-dimensional quantum clock. The setup is based on a programmable spatial light modulator which entangles the polarization and transverse spatial degrees of freedom of a single photon. It enables the simulation of a qubit history state containing the whole evolution of the system, capturing its main features in a simple and configurable scheme. We experimentally determine the associated system-time entanglement, which is a measure of distinguishable quantum evolution, and also the time average of observables, which in the present realization can be obtained through one single measurement.
D. Pabón, L. Rebón,S. Bordakevich, N. Gigena, A. Boette, C. Iemmi, R. Rossignoli,S. Ledesma
Physical Review A 99, 062333 (2019).
We propose a history state formalism for a Dirac particle. By introducing a reference quantum clock system it is first shown that Dirac’s equation can be derived by enforcing a timeless Wheeler-DeWitt-like equation for a global state. The Hilbert space of the whole system constitutes a unitary representation of the Lorentz group with respect to a properly defined invariant product, and the proper normalization of global states directly ensures standard Dirac’s norm. Moreover, by introducing a second quantum clock, the previous invariant product emerges naturally from a generalized continuity equation. The invariant parameter τ associated with this second clock labels history states for different particles, yielding an observable evolution in the case of a hypothetical superposition of different masses. Analytical expressions for both the space-time density and electron-time entanglement are provided for two particular families of electron states, the former including Pryce localized particles.
N. Diaz, R.Rossignoli
Physical Review D 99, 0454008 (2019).
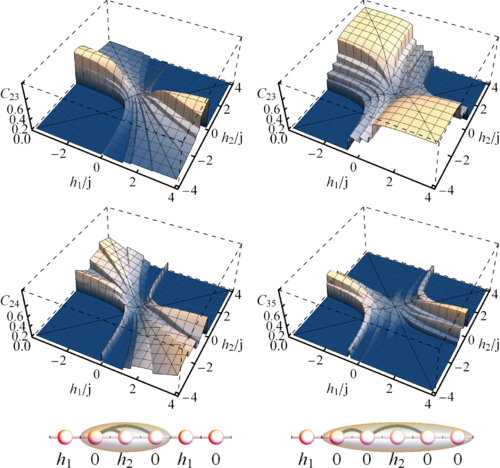
We analyze the phase diagram of the exact ground state (GS) of spin-s chains with ferromagnetic XXZ couplings under n-alternating field configurations, i.e., sparse alternating fields having nodes at n−1 contiguous sites. It is shown that such systems can exhibit a nontrivial magnetic behavior, which can differ significantly from that of the standard (n=1) alternating case and enable mechanisms for controlling their magnetic and entanglement properties. The boundary in field space of the fully aligned phase can be determined analytically ∀n, and shows that it becomes reachable only above a threshold value of the coupling anisotropy Jz/J, which depends on n but is independent of the system size. Below this value, the maximum attainable magnetization becomes much smaller. We then show that the GS can exhibit significant magnetization plateaus, persistent for large systems, at which the magnetization per site m obeys the quantization rule 2n(s−m)=integer, consistent with the Oshikawa, Yamanaka, and Affleck criterion. We also identify the emergence of field-induced spin polymerization, which explains the presence of such plateaus. Entanglement and field-induced frustration effects are also analyzed.
M. Cerezo, R.Rossignoli, N. Canosa, C.A. Lamas,
Physical Review B 99, 014409 (2019).
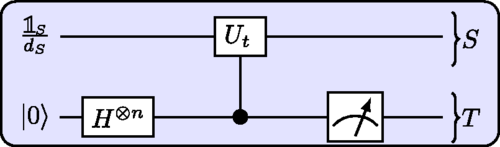
We discuss some fundamental properties of discrete system-time history states. Such states arise for a quantum reference clock of finite dimension and lead to a unitary evolution of system states when satisfying a static discrete Wheeler-DeWitt-type equation. We consider the general case where system-clock pairs can interact, analyzing first their different representations and showing there is always a special clock basis for which the evolution for a given initial state can be described by a constant Hamiltonian H. It is also shown, however, that when the evolution operators form a complete orthogonal set, the history state is maximally entangled for any initial state, as opposed to the case of a constant H, and can be generated through a simple double-clock setting. We then examine the quadratic system-time entanglement entropy, providing an analytic evaluation and showing it satisfies strict upper and lower bounds determined by the energy spread and the geodesic evolution connecting the initial and final states. We finally show that the unitary operator that generates the history state can itself be considered as an operator history state, whose quadratic entanglement entropy determines its entangling power. Simple measurements on the clock enable one to efficiently determine overlaps between system states and also evolution operators at any two times.
A. Boette, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 98, 032108 (2018).
We examine the fermionic entanglement in the ground state of the fermionic Lipkin model and its relation with bipartite entanglement. It is first shown that the one-body entanglement entropy, which quantifies the minimum distance to a fermionic Gaussian state, behaves similarly to the mean-field order parameter and is essentially proportional to the total bipartite entanglement between the upper and lower modes, a quantity meaningful only in the fermionic realization of the model. We also analyze the entanglement of the reduced state of four single-particle modes (two up-down pairs), showing that its fermionic concurrence is strongly peaked at the phase transition and behaves differently from the corresponding up-down entanglement. We finally show that the first measures and the up-down reduced entanglement can be correctly described through a basic mean-field approach supplemented with symmetry restoration, whereas the concurrence requires at least the inclusion of random-phase-approximation–type correlations for a proper prediction. Fermionic separability is also discussed.
M. Di Tullio, R. Rossignoli, M. Cerezo, N. Gigena
Physical Review A 100, 062104 (2019).
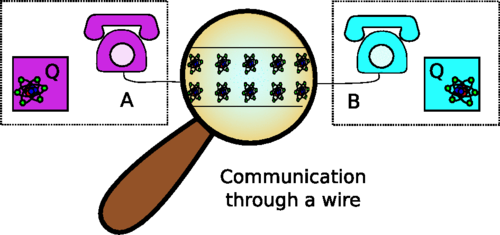
In this work (multipartite) entanglement, discord, and coherence are unified as different aspects of a single underlying resource theory defined through simple and operationally meaningful elemental operations. This is achieved by revisiting the resource theory defining entanglement, local operations, and classical communication (LOCC), placing the focus on the underlying quantum nature of the communication channels. Taking the natural elemental operations in the resulting generalization of LOCC yields a resource theory that singles out coherence in the wire connecting the spatially separated systems as an operationally useful resource. The approach naturally allows us to consider a reduced setting as well, namely, the one with only the wire connected to a single quantum system, which leads to discordlike resources. The general form of free operations in this latter setting is derived and presented as a closed form. We discuss in what sense the present approach defines a resource theory of quantum discord and in which situations such an interpretation is sound—and why in general discord is not a resource. This unified and operationally meaningful approach makes transparent many features of entanglement that in LOCC might seem surprising, such as the possibility to use a particle to entangle two parties, without it ever being entangled with either of them, or that there exist different forms of multipartite entanglement
D Egloff, J.M. Matera, T. Theurer, M.B. Plenio
Physical Review X 8, 031005 (2018).
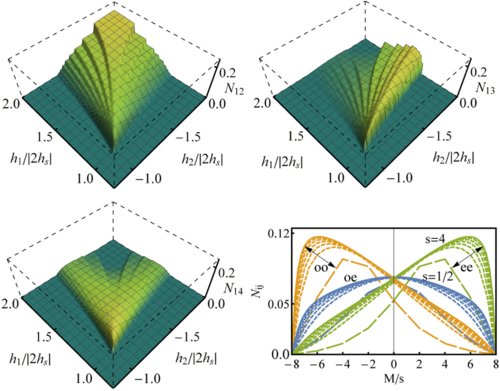
We analyze ground state (GS) factorization in general arrays of spins si with XXZ couplings immersed in nonuniform fields. It is shown that an exceptionally degenerate set of completely separable symmetry-breaking GSs can arise for a wide range of field configurations, at a quantum critical point where all GS magnetization plateaus merge. Such configurations include alternating fields as well as zero-bulk field solutions with edge fields only and intermediate solutions with zero field at specific sites, valid for d-dimensional arrays. The definite magnetization-projected GSs at factorization can be analytically determined and depend only on the exchange anisotropies, exhibiting critical entanglement properties. We also show that some factorization-compatible field configurations may result in field-induced frustration and nontrivial behavior at strong fields.
M. Cerezo, R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa, E. Ríos
Physical Review Letters 119 220605 (2017).
Full List
Separability and parity transitions in XYZ spin systems under nonuniform fields
N. Canosa, R. Mothe, and R. Rossignoli
Phys. Rev. A 101, 052103 (2020).
History state formalism for scalar particles
N. L. Diaz, J. M. Matera, and R. Rossignoli
Phys. Rev. D 100, 125020 (2019).
Conditional states and entropy in qudit-qubit systems
M. Bilkis, N. Canosa, R.Rossignoli, N. Gigena
Physical Review A 99, 062119 (2019).
Parallel-in-time optical simulation of history states
D. Pabón, L. Rebón,S. Bordakevich, N. Gigena, A. Boette, C. Iemmi, R. Rossignoli,S. Ledesma
Physical Review A 99, 062333 (2019).
History state formalism for Dirac’s theory
N. Diaz, R.Rossignoli
Physical Review D 99, 0454008 (2019).
Inducing critical phenomena in spin chains through sparse alternating fields
M. Cerezo, R.Rossignoli, N. Canosa, C.A. Lamas,
Physical Review B 99, 014409 (2019).
History states of systems and operators
A. Boette, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 98, 032108 (2018).
Fermionic entanglement in the Lipkin model
M. Di Tullio, R. Rossignoli, M. Cerezo, N. Gigena
Physical Review A 100, 062104 (2019).
Fermionic entanglement in superconducting systems
M. Di Tullio, N. Gigena, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 97, 062109 (2018).
Of Local Operations and Physical Wires
D Egloff, J.M. Matera, T. Theurer, M.B. Plenio
Physical Review X 8, 031005 (2018).
Complexity of a matter-field Hamiltonian in the vicinity of a quantum instability
A.M. Kowalski, A. Plastino, R. Rossignoli
Physica A 513, 767 (2019).
Nonlinear dynamics of a semiquantum Hamiltonian in the vicinity of quantum unstable regimes
A.M. Kowalski, R. Rossignoli
Chaos, Solitons and Fractals 109, 140 (2018).
Spectrum and normal modes of non-Hermitian quadratic boson operators
Javier Garcia, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 96, 062130 (2017).
Factorization and criticality in finite XXZ systems of arbitrary spin
M. Cerezo, R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa, E. Ríos
Physical Review Letters 119 220605 (2017).
Determination of any pure spatial qudits from a minimum number of measurements by phase-stepping interferometry
A. Pears Stefano, L. Rebón, S. Ledesma, C. Iemmi
Physical Review A 96, 062328 (2017).
Quantum Discord and Entropic Measures of Quantum Correlations”:” Optimization and Behavior in Finite XY Spin Chains
N. Canosa, M. Cerezo, N. Gigena, R. Rossignoli
Lectures on General Quantum Correlations and their Applications, p. 455, Springer (2017).
Bipartite entanglement in fermion systems
N. Gigena, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 95 062320 (2017).
Entanglement and coherence in a spin-s XXZ system under non-uniform fields
E. Ríos, R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa
Journal of Physics B 50 095501 (2017).
Pair entanglement in dimerized spin-s chains
A. Boette, R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa, J.M. Matera
Physical Review B 94 214403 (2016).
Factorization in spin systems under general fields and separable ground-state engineering
M. Cerezo, R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa
Physical Review A 94 042335 (2016).
One-body information loss in fermion systems
N. Gigena, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 94 042315 (2016).
Conditional purity and quantum correlation measures in two qubit mixed states
L. Rebon, R. Rossignoli, J.J.M. Varga, N. Gigena, N. Canosa, C. Iemmi, S. Ledesma
Journal of Physics B 49 215501 (2016).
Coherent control of quantum systems as a resource theory
J. M. Matera, D. Egloff, N. Killoran, M. B. Plenio
Quantum Science and Technology 1, 01LT01 (2016).
System-time entanglement in a discrete time model
A. Boette, R. Rossignoli, N. Gigena, M. Cerezo
Physical Review A 93, 062127 (2016).
Nontransverse factorizing fields and entanglement in finite spin systems
M. Cerezo, R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa
Physical Review B 92, 224422 (2015).
Entanglement in fermion systems
N. Gigena, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 92 042326 (2015).
Exact dynamics and squeezing in two harmonic modes coupled through angular momentum
N. Canosa, S. Mandal, R. Rossignoli
Journal of Physics B 48 165501 (2015).
Generalized mean-field description of entanglement in dimerized spin systems
A. Boette, R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa, J.M. Matera
Physical Review B 91 064428 (2015).
Dimerized ground states in spin-S frustrated systems
C.A. Lamas, J.M. Matera
Physical Review B 92 115111 (2015).
Quantum discord and information deficit in spin chains
N. Canosa, L. Ciliberti, R. Rossignoli
Entropy 17 1634 (2015).
Generalized conditional entropy optimization for qudit-qubit states
N. Gigena, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 90 042318 (2014).
Dynamics of entanglement between two harmonic modes in stable and unstable regimes
L. Rebon, N. Canosa, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 89 042312 (2014).
Phase diagram study of a dimerized spin-S zig-zag ladder
J M Matera and C A Lamas
Journal of Physics :Condensed Matter 26 326004 (2014).
Generalized conditional entropy in bipartite quantum systems
N. Gigena, R. Rossignoli
Journal of Physics A :Math.Theor. 47 (2014) 015302.
Phase-Measurement Interferometry as a Simulation of Optimal Quantum-State Tomography
L. Rebón, C. Iemmi and S. Ledesma
Optik 124 (2013) 5548-5552.
Discord and information deficit in the XX chain
L. Ciliberti, N. Canosa, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 88 (2013) 012119.
Preparing arbitrary pure states of spatial qudits with a single phase-only spatial light modulator
A. Solas-Prosser, A. Arias, J. J. M. Varga, L. Rebón, S. Ledesma, C. Iemmi and L. Neves
Optics Letters / Vol. 38, No. 22 (2013).
Quantum discord and related measures of quantum correlations in finite XY chains
N. Canosa, L. Ciliberti, R. Rossignoli
Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 27 (2013) 1345033.
Concepts and Recent Advances in Generalized Information Measures and Statistics
A. M. Kowalski, R. Rossignoli, E. M. F. Curado
Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 27 (2013) 1345033. Bentham eBooks ISBN 978-1-60805-761-0 (2013).
Majorization and Generalized Entropies
N. Canosa, R. Rossignoli,
Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 27 (2013) 1345033. P. 100 in Concepts and Recent Advances in Generalized Information Measures and Statistics Bentham eBooks 978-1-60805-761-0 (2013).
Essentials of Information Entropy and Related Measures
R. Rossignoli, A. M. Kowalski, E. M. F. Curado,
P. 30 in Concepts and Recent Advances in Generalized Information Measures and Statistics Bentham eBooks ISBN 978-1-60805-761-0 (2013).
Heat and Entropy :A brief history
E. M. F. Curado, A. M. Kowalski, R. Rossignoli,
Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 27 (2013) 1345033. P. 3 in Concepts and Recent Advances in Generalized Information Measures and Statistics Bentham eBooks ISBN 978-1-60805-761-0 (2013).
Entanglement and area laws in weakly correlated gaussian states
J. M. Matera, R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa
Physical Review A 86 (2012) 062324.
Measurements, quantum discord and parity in spin 1 systems
R. Rossignoli, J.M. Matera, N. Canosa
Physical Review A 86 (2012) 022104.
Quantum Correlations and least disturbing local measurements,
R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa, L. Ciliberti,
Physical Review A 84 (2011) 052329.
Entanglement between two harmonic modes coupled by angular momentum
L. Rebón, R. Rossignoli
Physical Review A 85 (2011) 052320.
Even-odd entanglement in boson and spin systems
R. Rossignoli, N. Canosa, J.M. Matera,
Physical Review A 83 (2011) 042328.
Theses
Correlaciones cuánticas y campos factorizantes en sistemas de espines (Quantum correlations and factorizing fields in spin systems)
Marco Cerezo de la Roca. Adv. :R. Rossignoli
Graduate Thesis, UNLP (2015)
Medidas entrópicas generalizadas de correlaciones cuánticas (Generalized entropic measures of quantum correlations)
Leonardo Ciliberti. Adv. :R. Rossignoli and N. Canosa
Ph.D. Thesis, UNLP (2015).
Descripción de correlaciones cuánticas a partir de aproximaciones de campo medio generalizadas (Description of quantum correlations through generalized mean field treatments)
A. Boette. Adv. :R. Rossignoli, CoAdv. :J.M. Matera
Graduate Thesis, UNLP (2014).
Entrelazamiento Cuántico en Sistemas de Muchos Cuerpos (Quantum Entanglement in Many-Body Systems)
J.M. Matera Adv. :R. Rossignoli
Ph.D. Thesis, UNLP (2011).